The Inert Gas (IG) System and FM-200(HFC-277ea) are both fire suppression systems, but they differ significantly in their composition, operation, and applications.
1. Composition of Suppression Agents
• Inert Gas (IG) System: Uses a combination of natural gases like nitrogen, argon, and sometimes a small amount of CO₂. It does not involve chemical agents and is environmentally safe.
• FM-200: Uses heptafluoropropane, a chemical gas, as the suppression agent. FM-200 is a clean agent that is effective for sensitive equipment, but it is a man-made substance.
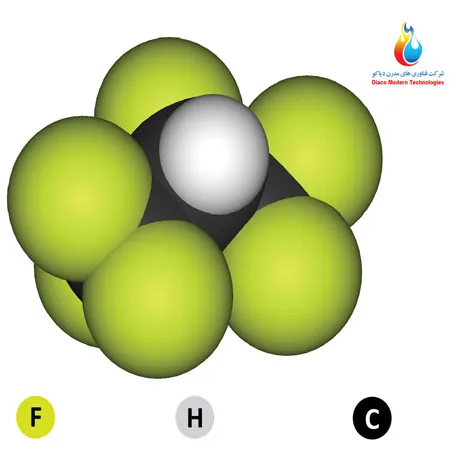
2. Method of Fire Suppression
• IG System: Lowers the oxygen concentration in the protected area to a level below that required for combustion (usually between 12-15% oxygen). Humans can still breathe at this level, but fire cannot sustain itself.
• FM-200: Absorbs heat from the fire, disrupting the combustion process on a molecular level. FM-200 works quickly to put out fires without significantly reducing oxygen, making it safer for occupied spaces.
3. Environmental Impact
• IG System: Environmentally friendly, as it uses naturally occurring gases without an impact on the ozone layer or greenhouse effect.
• FM-200: While FM-200 is a clean agent and leaves no residue, it is a hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) and has a moderate global warming potential. It does not harm the ozone layer but can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
4. Applications
• IG System: Commonly used in large data centers, power plants, and places where people may not be present, as the lower oxygen levels can be uncomfortable over extended periods.
• FM-200: Widely used in data centers, telecom facilities, museums, and libraries, as it is safe for use in occupied spaces and does not leave residue.

5. Storage and Discharge Requirements
• IG System: Requires more storage space because it needs large, high-pressure cylinders for the inert gases, which are stored at very high pressures (200-300 bar).
• FM-200: Requires less storage space since the chemical agent is more concentrated. The system typically operates at lower pressures (around 25-42 bar), making it easier to store in smaller spaces.
Summary
• Inert Gas System: Natural, reduces oxygen, environmentally friendly, large storage needs, effective for unoccupied areas.
• FM-200: Chemical agent, heat-absorbing, minimal oxygen impact, smaller storage, and effective for occupied areas.
Each system has its advantages depending on the specific fire protection needs and environmental priorities.
When considering the future viability of fire suppression systems like the Inert Gas (IG) System and FM-200, it’s important to assess environmental, regulatory, and technological factors:
1. Environmental Impact and Regulations
• Inert Gas (IG) Systems: Because these systems use naturally occurring gases like nitrogen and argon, they have zero ozone depletion potential and a very low impact on global warming. They’re also non-toxic and safe for the environment, which aligns with global environmental goals to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. As more stringent regulations are introduced to phase out systems with higher environmental impacts, IG systems are expected to remain compliant and continue growing in use.

• FM-200: This is a hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) with moderate global warming potential (GWP). Although it is effective and widely used, regulatory bodies are increasingly pushing to phase out or restrict HFCs due to their greenhouse impact. The EU, for example, has strict F-gas regulations that could lead to reductions in FM-200 use over time, and other regions may follow.
• Future Advantage: The IG System is more sustainable in the long term due to its minimal environmental impact. FM-200 may face regulatory challenges that could limit its use in the future.
2. Safety for Occupied Spaces
• IG System: Inert gas systems reduce oxygen levels, which can make extended exposure uncomfortable or even hazardous for people in protected spaces. However, advancements in delivery systems are improving how inert gases are released, potentially minimizing the risk in occupied areas.
• FM-200: This is widely considered safe for use in occupied spaces, as it suppress fire without reducing oxygen levels significantly. This makes it especially useful for places where people are present, like data centers, museums, and offices.
• Future Advantage: FM-200’s safety profile for occupied areas keeps it relevant, but alternative systems with low-GWP agents are emerging, which may offer both environmental and safety benefits.
3. Technological Advancements and Alternatives
• IG Systems: With growing interest in eco-friendly solutions, inert gas systems could see innovation in system efficiency, compactness, and delivery mechanisms. Additionally, new combinations of inert gases may make these systems safer for more environments.
• FM-200: The industry is actively exploring alternatives to FM-200, such as new HFC-free clean agents with lower environmental impact, like Novec 1230 (an FK-5-1-12 clean agent). These alternatives aim to replicate FM-200’s effectiveness while avoiding regulatory issues.
• Future Advantage: IG Systems may lead for eco-friendly applications, while new clean agents may gradually replace FM-200 in some markets.
4. Market Demand and Adaptability
Companies increasingly prefer sustainable, future-proof solutions that meet evolving regulations and environmental standards. IG systems have a strong market outlook due to their compatibility with these trends.
FM-200 may remain relevant for a while, but the demand for greener alternatives could limit its long-term growth.
In summary, FM-200 systems are faster in suppression fires, which is advantageous in high-risk environments. However, both systems are effective, with the choice depending on the specific needs of the protected area.